Variants Caller:选择了GATK中的HaplotypeCaller、Mutech2以及VarScan这三种软件进行比较(你可以选择你想要任意的软件比较)
数据模拟软件选择:一般评估软件的功能都会应用到一些数据模拟软件,不同的模拟软件应用的场景和功能也都大相径庭,目前比较流行的是ART(负责模拟fastq文件)
因为没有做过类似的工作,加上本身能力有限,水平一般,遇到问题首先肯定是需要Google一下 的(不要问我为什么不用国产浏览器,你懂得~)。通过查阅相关文献,了解了关于数据模拟相关的文献和进展。如下
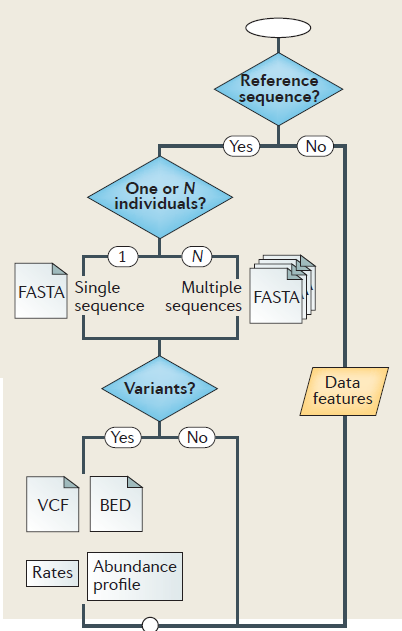
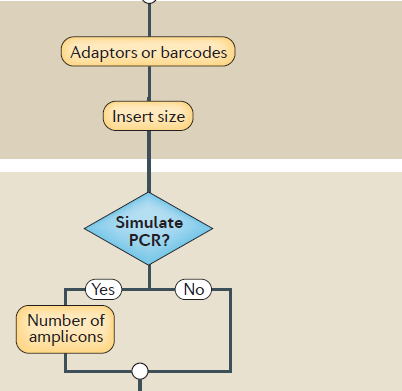
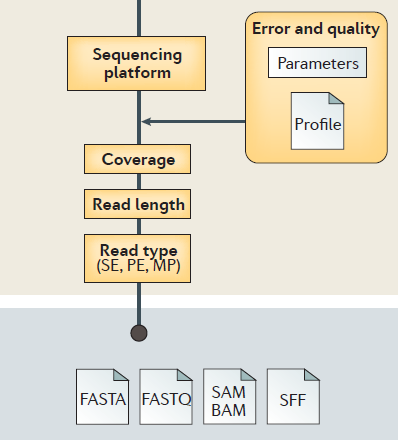
参考文献 :
A comparison of tools for the simulation of genomic next-generation sequencing data
差不多类似这样的一个workflow,作为整个模拟的流程(有时间可以好好阅读上述文献,蛮受用的)
步骤:
1. 利用SCNVSim模拟出Tumor genome(知道特定位点以及突变信息) 2. 使用ART模拟软件可以得到相应的fastq文件(测序仪器类型;测序的类型read1, read2;reads的长度;模板的片段长度;测序深度等) 3. 正常基因组fastq和模拟出的Tumor genome的fastq文件进行混合(根据ART给定不同的reads深度叠加) 4. Pipeline running(这里可以比较不同的variants calling software,前期的流程大致一样) 5. 比较variants结果(sensitivity,specificity等)
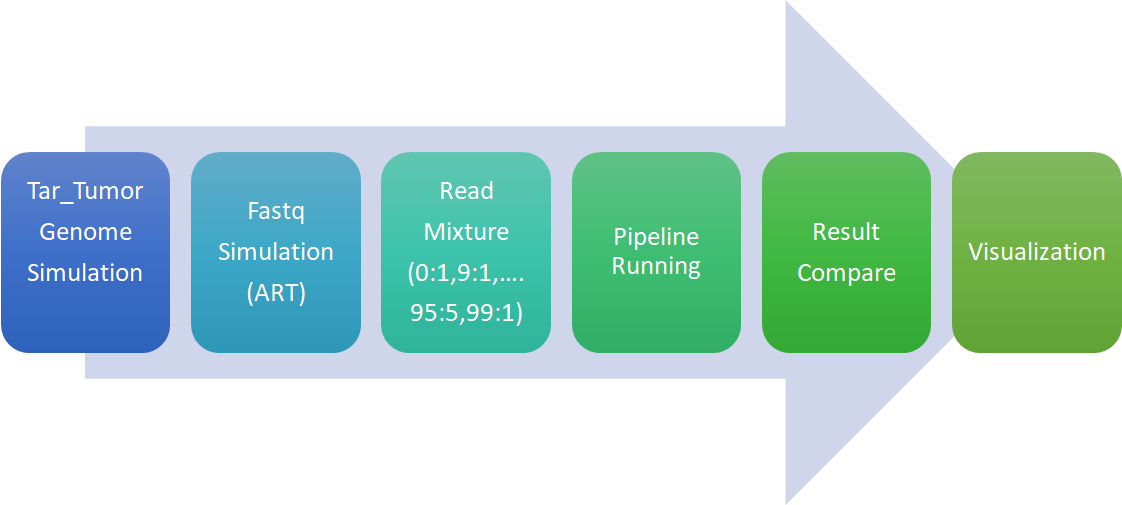
fastq数据模拟、处理流程图
TIPS:在模拟肿瘤基因组的过程中,因为服务器的储存空间有限,所以在第一步的时候不能使用参考基因组进行模拟,而选择了靶向数据。但是,SCNVSim并不支持靶向数据的模拟,因而在模拟肿瘤基因组的过程中需要自己编写脚本对参考基因组进行处理。
代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/python2.7
#=========================================================================================
# Simulate a target mutation from a given fasta
# Usage:
# python simulate.py -fi target.fa
#
# Contributor: RaymonTian
# Date:2019-09-02
#
#=========================================================================================
import sys
import random
import argparse
import os
import time
start = time.clock()
class Simu_Fasta(object):
def __init__(self, Infile):
''' read raw fasta
'''
if Infile[-3:] == '.gz':
self.tar_fa = gzip.open(Infile, 'rb')
else:
self.tar_fa = open(Infile, 'r')
#return self.tar_fa
def Simu_fa(self):
''' simulate fasta and corresponding mutated information
'''
simu_fa = list()
simu_vcf = list()
for Line in self.tar_fa:
Line = Line.upper()
if Line.startswith('>'):
## progress header
header, chrom, start = Header_line(Line)
else:
mut_line, pos, base, mut, tag = Mut_line(Line, start)
p = random.uniform(0,1)
## ratio het/hm
if p >= 0.5:
line = Reverse_Com(mut_line)
genotype = '1/1'
else:
line = Line.rstrip()
genotype = '0/1'
simu_fa.append(header + '-Forward' + '\n' + mut_line + '\n' + header + '-Reverse' + '\n' + line + '\n')
simu_vcf.append(chrom + '\t' + str(pos) + '\t' + base + '\t' + mut + '\t' + tag + '\t' + genotype + '\t' + header + '\n')
return simu_fa, simu_vcf
def close(self):
self.tar_fa.close()
def Header_line(Line):
''' >chr1:10000-12000\n
chr start end
chr1 10000 12000
'''
header = Line.rstrip()
chrom = header.split(':')[0][1:]
start = int(header.split(':')[1].split('-')[0]) + 1
return header, chrom, start
def Mut_line(Line, start):
''' Progress each line in fasta
snv and indel
'''
line = Line.rstrip()
line_len = len(line)
### random pos
rand_idx = random.randint(0, line_len -1)
base = line[rand_idx]
## add snv or indel according random p value
p = random.uniform(0,1)
## Defination a ratio between snv and indel
## Here snv : indel = 9 : 1
if p < 0.9:
## snv simulation
mut = SNV_simu(base)
mut_line = line[:rand_idx] + mut + line[rand_idx + 1:]
tag = 'snv'
else:
## indel simulation
mut, mut_line, tag, base = Indel_simu(line, rand_idx, base)
pos = start + rand_idx
return mut_line, pos, base, mut, tag
def SNV_simu(base):
''' simulate snv in this line
'''
if not base in ['A', 'T', 'C', 'G']:
sys.stderr.write('The base is not one of "[ATCG]" but %s' %(base))
return ''
p = random.uniform(0,1)
if base in ['A', 'T']:
if p >= 0.5:
base = 'C'
else:
base = 'G'
elif base in ['C', 'G']:
if p >= 0.5:
base = 'A'
else:
base = 'T'
return base
def Indel_simu(line, rand_idx, base):
''' simulate insertion and deletion
'''
p = random.uniform(0,1)
if p < 0.5:
## insertion 1:4
ins_len = random.randint(1,4)
ins_seq = list()
while 1:
if ins_len == 0: break
p = random.uniform(0,1)
if p >= 0.75:
A = 'A'
elif p >= 0.5 and p < 0.75:
A = 'T'
elif p >= 0.25 and p < 0.5:
A = 'C'
else:
A = 'G'
ins_seq.append(A)
ins_len -= 1
base = base
mut = base + ''.join(ins_seq)
mut_line = line[:rand_idx + 1] + ''.join(ins_seq) + line[rand_idx + 1:]
tag = 'insertion'
else:
## deletion 1:4
del_len = random.randint(1,4)
if del_len + rand_idx > len(line):
##
mut = line[rand_idx:]
mut_line = line[:rand_idx]
else:
mut = line[rand_idx:rand_idx + del_len]
mut_line = line[:rand_idx] + line[rand_idx + del_len:]
base = line[rand_idx - 1] + mut
mut = line[rand_idx - 1]
tag = 'deletion'
return mut, mut_line, tag, base
def Reverse_Com(seq):
''' Get the reverse complement reads form given seq
'''
dict = {'A':'T', 'T':'A', 'C':'G', 'G':'C', 'a':'t', 't':'a', 'c':'g', 'g':'c', 'N':'N'}
##
new_seq = []
for i in list(seq):
new_seq.append(dict[i])
return ''.join(new_seq)
def Make_dir(out_dir):
''' make a directory if not exist
'''
if not os.path.exists(out_dir):
os.makedirs(out_dir)
return os.path.abspath(out_dir)
def File_write(out_dir, simu_fa, simu_vcf):
''' >chr1:100-200-Forward
AGTAGATCTACAGGCATACTAGGTAGATGAAT
>chr1:100-200-Reverse
TCATCTAGATGTCCGTATGATCCATCTACTTA
'''
path_dir = Make_dir(out_dir)
tumor_fa = open(path_dir + '/' + 'Tumor_simu.fa', 'w')
vcf_file = open(path_dir + '/' + 'mut.vcf', 'w')
for i in simu_fa:
tumor_fa.write(i)
for i in simu_vcf:
vcf_file.write(i)
tumor_fa.close()
vcf_file.close()
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description = 'Simulate a target fasta')
parser.add_argument('-fi', '--target_fasta', help= 'The fasta file from normal sample')
parser.add_argument('-o', '--out_dir', help= 'The output floder with mutated txt and simulated fasta')
args = parser.parse_args()
out_dir = Make_dir(args.out_dir)
if not (args.target_fasta or out_dir):
sys.stderr.write('\nError:\n\tParamenters Lacking!!!\n')
sys.stdout.write('\nNote:\n\tPlease use "python simula_SI.py -h" as a guider.\n\n')
sys.exit(-1)
tar_fa = Simu_Fasta(args.target_fasta)
simu_fa, simu_vcf = tar_fa.Simu_fa()
File_write(out_dir, simu_fa, simu_vcf)
tar_fa.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
end = time.clock()
print 'Time Spent:',(end-start)
1.模拟肿瘤靶向基因组
- 首先从全外exon.bed文件中随机选取500个bed区域,前后延申200bp
- 利用bedtools getfasta得到参考基因组靶向tar.fa
- 利用python simulate.py -fi tar.fa得到模拟后的tumor.fa和对应的mut.vcf
------------------------------------------------------
•Random 482 WES exon region , +- 200 bp
•SNV:INDEL 9:1
•SNV 438(ATCG)
•INDEL 44(Insertion 20,Deletion 24) length(1-4bp)
•Homogeneous :Heterozygote 1:1
•Depth 1000X
•Purity: 100%, 90%, 80%, 60%, 50%, 30%, 10%, 5%, 1%
------------------------------------------------------
2.模拟不同浓度的fastq文件
- 根据ART对tar.fa和tumor.fa分别进行深度模拟得到fq
- 总深度不变为1000X,根据不同的fq混合模拟得到的肿瘤浓度依次分别为:100%,90%,80%,60%,50%,30%,10%,5%,1%
3.Pipeline Running
- QC:fastqc
- Alignment;BWA mem
- Bam pre-progress :GATK Markdup;BQSR。。。。
- Calling:HaplotypeCaller, Mutect2, Varscan
4.比较结果和可视化
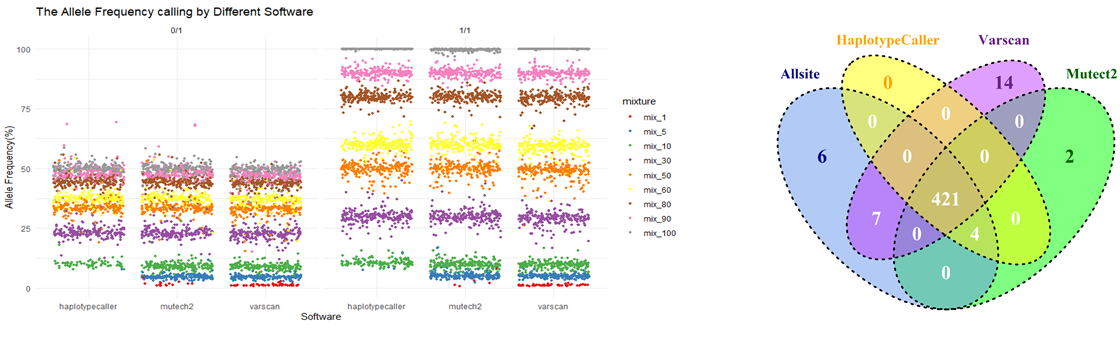
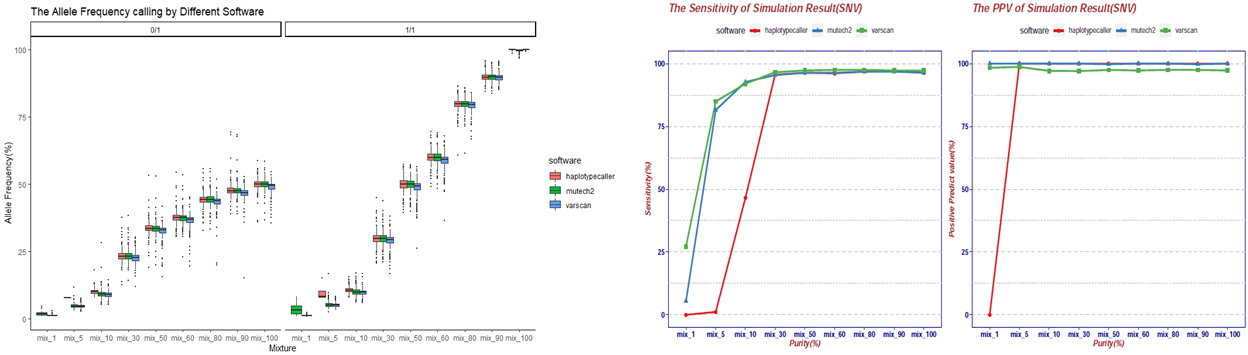
从上图得出:三个软件在高肿瘤浓度(>30%)的情况下检出率都在90%以上;在对SNV的calling中,varscan相对于其他两个软件在低浓度下能够有较高的检出率,但是在高浓度下的假阳性相对较高。
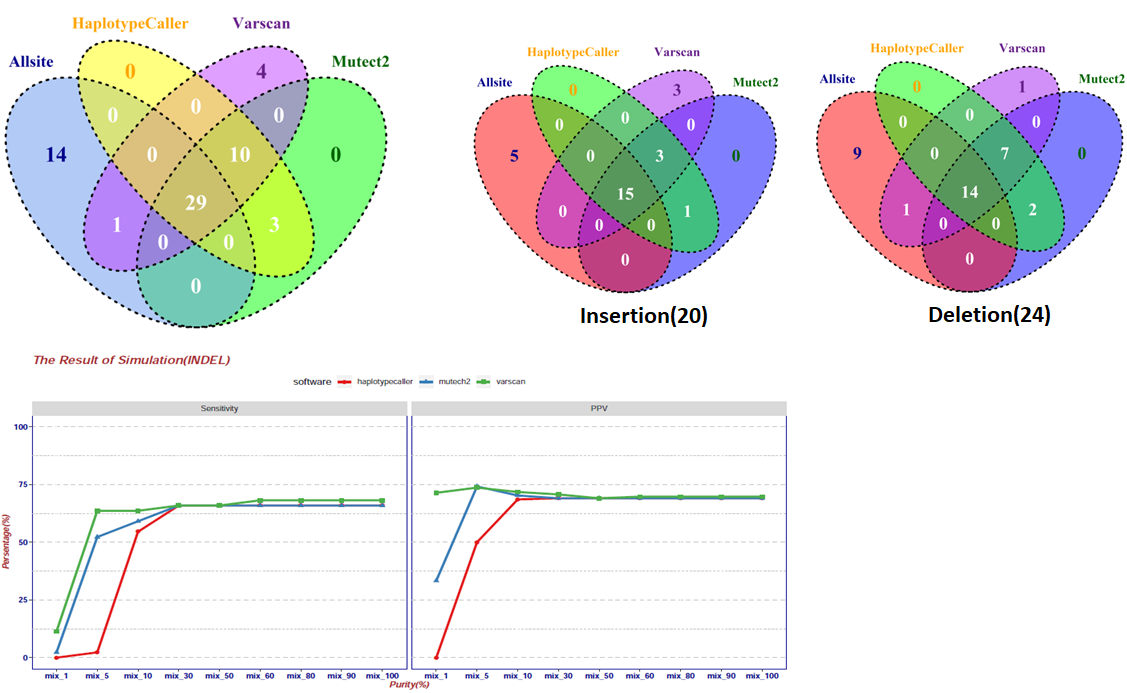
VENN图从左到右一次是所有indel的检出情况、insertion检出、deletion检出。其中可以看出,haplotypecaller 和 Mutect得到的indel检出一致率很高,同时在这三种不同的软件中,insertion的检出要高于deletion(可能是因为突变的序列导致的)。折线图中可见随着浓度的上升,indel的检出率上升。但是在高浓度下,indel的检出持续在70%左右,仍然有一部分indel未检出;在低浓度下varscan和mutect2相对效果好。
问题:在进行INDEL检出的过程中发现了一些比较有意思的现象,如上述折线图,indel的检出率相对于SNV要低的多,到底是什么原因导致的呢?
在评估indel的同时,发现软件在距离突变位点上下几bp检测到了indel,但是indel的内容和突变的不一样。例如下图中存在的情况,导致检测的结果有出入。
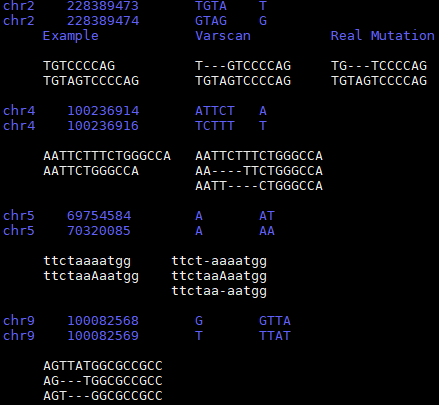
因而,indel的检出相比snv要复杂,一般需要溯回检测是否存在,以及确认具体的突变的情况。
结论
不同的软件基于的算法不同,因而在同样的数据下会产生一些不同的结果。在数据分析中,需要根据数据类型来不断的调整参数或者多软件进行比较,能够更为精确地call出突变。另外,对于indel的处理相比snv要更为谨慎。








评论 (0)